Introduction:
At RALLY, we specialize in delivering precision-engineered aluminum parts tailored to meet the exacting standards of diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and medical devices. Our expertise in CNC machining and commitment to quality ensures that every part we produce meets your specifications and performance requirements.
Whether you need a prototype or a large production run, our team is dedicated to providing high-quality, customized aluminum components. This guide will walk you through the process of making aluminum parts, offering valuable insights for your manufacturing needs.
Key Takeaways:
Understanding the process of making aluminum parts using CNC machining and other techniques.
1. Introduction to Aluminum Part Manufacturing
1.1 Overview of Aluminum Manufacturing
Aluminum manufacturing is crucial across various industries due to aluminum’s unique properties, such as being lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly conductive. This process involves extracting aluminum from its ore, refining it, and then fabricating it into parts using techniques like extrusion, casting, and machining.
The versatility of aluminum allows it to be used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction, where it enhances performance and efficiency while maintaining strength and durability. Aluminum’s recyclability further adds to its environmental benefits, making it a sustainable choice for numerous applications.
1.2 Applications of Aluminum Parts
Aluminum parts are widely used in various industries, including automotive for engine components and body panels, aerospace for structural elements, electronics for heat sinks and casings, and construction for window frames and cladding due to their lightweight, durability, and corrosion resistance. Aluminum parts are utilized in diverse applications, including:
Automotive Applications
| Component | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Parts | Lightweight, heat resistance | Cylinder heads, pistons |
| Body Structures | Crashworthiness, weight reduction | Car frames, body panels |
| Wheels | Aesthetic appeal, strength | Alloy wheels, rims |
Aerospace Applications
| Component | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Frames | High strength-to-weight ratio, durability | Wing structures, fuselages |
| Engine Components | Heat resistance, lightweight | Turbine blades, engine housings |
| Structural Parts | Corrosion resistance, reliability | Landing gear, control surfaces |
Electronics Applications
| Component | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Sinks | Excellent thermal conductivity | CPU coolers, power transistors |
| Casings | Lightweight, aesthetic appeal | Smartphone bodies, laptop shells |
| Connectors | Electrical conductivity, durability | USB ports, battery connectors |
2. Understanding Aluminum: Properties and Grades
2.1 Characteristics of Aluminum
Aluminum is renowned for its unique properties that make it a highly sought-after material in various industries. It is lightweight, with a density of about one-third that of steel, which contributes to its extensive use in applications where reducing weight is crucial.
This metal is inherently corrosion-resistant due to a thin oxide layer that forms on its surface, providing protection against environmental factors.

2.2 Aluminum Grades and Their Uses
Aluminum comes in various grades, each suited to different applications based on its composition and properties. The following table provides an overview of common aluminum series and their typical uses:
| Aluminum Series | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 Series | Pure aluminum (99% or higher), excellent corrosion resistance, and high thermal conductivity | Electrical applications, chemical equipment, and food processing industries |
| 2000 Series | Aluminum-copper alloys, known for high strength and excellent machinability | Aerospace components, truck wheels, and high-stress structural applications |
| 3000 Series | Aluminum-manganese alloys, offering good corrosion resistance and moderate strength | Beverage cans, roofing sheets, and heat exchangers |
| 4000 Series | Aluminum-silicon alloys, characterized by good wear resistance and low thermal expansion | Automotive pistons, engine blocks, and manufacturing tools |
| 5000 Series | Aluminum-magnesium alloys, known for high strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability | Marine applications, pressure vessels, and automotive body panels |
| 6000 Series | Aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys, offering good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance | Structural applications, architectural framing, and bridge components |
| 7000 Series | Aluminum-zinc alloys, known for the highest strength among aluminum alloys | Aerospace frames, sports equipment, and military vehicles |
3. Preparing for Aluminum Fabrication
3.1 Essential Materials

To successfully fabricate aluminum parts, you need to have the right materials on hand. Here’s a list of essential materials you might need:
- Aluminum Sheets: Used for creating flat parts or components.
- Aluminum Rods: Ideal for structural elements and supports.
- Aluminum Tubes: Commonly used for frames and piping.
- Aluminum Plates: Used in applications requiring thicker material.
- Fasteners and Connectors: Screws, bolts, and nuts specifically designed for aluminum.
3.2 Overview of Basic Tools

Having the correct tools is equally important to ensure precision and efficiency in aluminum fabrication. Here’s an overview of the basic tools required:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Saw | Used for cutting aluminum sheets, rods, and tubes to the desired dimensions. |
| Drill | Essential for creating holes and slots in aluminum parts for assembly or other purposes. |
| Deburring Tool | Removes sharp edges and burrs from cut or drilled aluminum parts, ensuring smooth finishes. |
| Bending Machine | Used to bend aluminum sheets and rods into specific shapes without breaking or cracking. |
| Welder | Required for joining aluminum parts together securely, especially in structural applications. |
| CNC Machine | Offers precision cutting, shaping, and engraving for complex and detailed aluminum parts. |
| Clamps | Holds aluminum parts securely in place during cutting, drilling, or welding processes. |
| Polishing Tools | Buffs and polishes aluminum surfaces for a finished look and added protection. |
Get Your CNC Parts Into Production Today
Your Global Partner for Quality CNC Machining Services in China!
4. Major Aluminum Fabrication Processes
4.1 CNC Machining
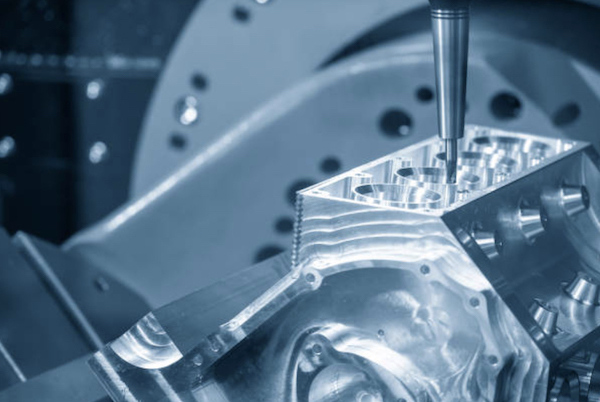

Description of CNC Machining: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining utilizes computer-controlled tools to precisely remove material from aluminum, creating intricate and accurate parts. This process is ideal for high-precision applications where complex geometries are required.
Advantages and Applications:
- Advantages: High precision, repeatability, and capability to produce complex shapes.
- Applications: Widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries for components such as engine parts, brackets, and housings.
Considerations and Tips:
- Tool Selection: Use tools specifically designed for aluminum to prevent material damage.
- Machine Maintenance: Regular maintenance and calibration of CNC machines are essential for consistent accuracy.
- Optimization: Adjust feed rates and speeds to avoid overheating and ensure smooth finishes.
4.2 Aluminum Extrusion
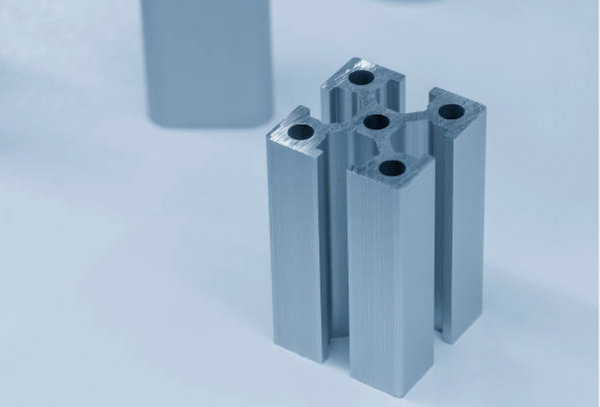
Description of the Extrusion Process: Extrusion involves pushing aluminum through a die to create long shapes with consistent cross-sections. This process is efficient for producing uniform profiles.
Benefits and Limitations:
- Benefits: High efficiency, uniformity, and capability to produce complex cross-sectional shapes.
- Limitations: Limited to shapes determined by the die and potential for surface defects if not properly managed.
Typical Uses:
- Applications: Structural components, frames, heat sinks, and railings.
4.3 Sheet Metal Fabrication
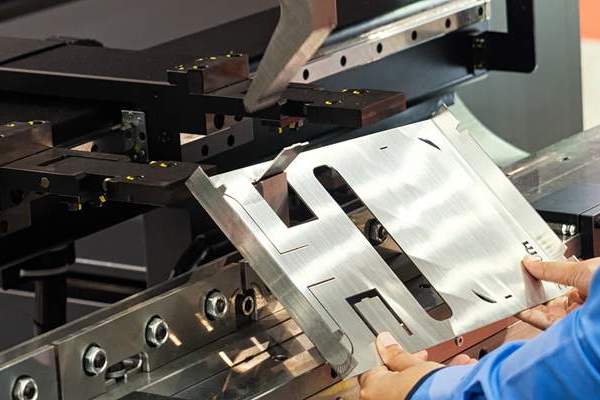

Methods Involved:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | Uses a laser to precisely cut aluminum sheets with minimal waste. |
| Punching | Creates holes and shapes in aluminum sheets using a punch press. |
| Bending | Forms angles and curves in aluminum sheets using a press brake or similar equipment. |
Benefits of Sheet Metal Fabrication:
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications from prototypes to high-volume production.
- Cost-Effective: Efficient material usage and lower production costs.
Common Applications:
- Uses: Enclosures, brackets, panels, and other custom parts.
4.4 Aluminum Casting
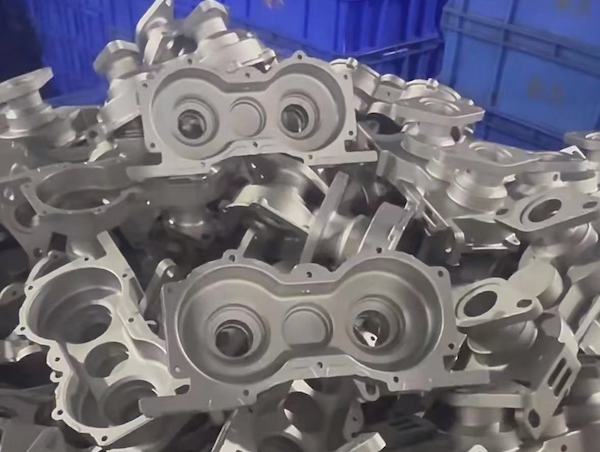

Overview of Molding and Casting Techniques: Casting involves pouring molten aluminum into molds to create parts. Various casting techniques include sand casting, die casting, and investment casting.
Advantages and Considerations:
- Advantages: Ability to produce complex geometries and large parts.
- Considerations: Requires careful control of temperature and mold quality to ensure consistent results.
Industry Applications:
- Applications: Engine components, machinery parts, and decorative items.
4.5 Aluminum Forging

Explanation of the Forging Process: Forging involves shaping aluminum under high pressure, typically using a hammer or press. This process enhances the strength of the aluminum by aligning its grain structure.
Benefits and Limitations:
- Benefits: Produces high-strength parts with superior mechanical properties.
- Limitations: Generally limited to simpler shapes and smaller parts.
Common Applications:
- Uses: Aerospace components, automotive parts, tools, and hardware.
4.6 3D Printing of Aluminum Parts
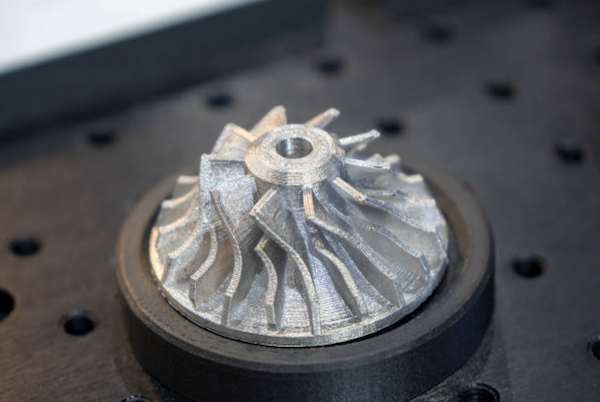

Introduction to 3D Printing Technology: 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds parts layer by layer from digital models. This technology allows for the creation of highly complex and customized parts.
Benefits of 3D Printing for Aluminum Parts:
- Flexibility: Ability to produce intricate designs and rapid prototyping.
- Efficiency: Reduces material waste compared to traditional subtractive methods.
Emerging Applications and Future Potential:
- Applications: Custom medical implants, aerospace components, and innovative design solutions. The future of 3D printing in aluminum fabrication holds great potential for creating more complex and lightweight structures with improved performance.
5. Surface Treatment and Protection Techniques
Surface treatment and protection techniques are essential in enhancing the durability, appearance, and performance of aluminum parts. Here are some common methods:
5.1 Anodizing
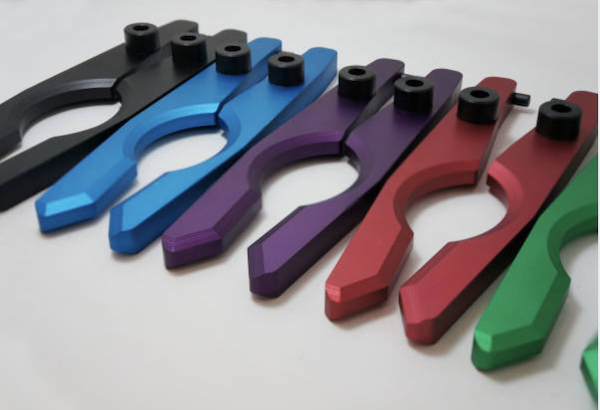

Process and Benefits of Anodizing Aluminum: Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances the natural oxide layer on the surface of aluminum, providing increased corrosion resistance and a decorative finish.
Benefits:
- Durability: Significantly improves corrosion resistance.
- Aesthetic: Offers a range of colors and finishes.
- Protection: Enhances wear resistance and surface hardness.
5.2 Painting and Coating

Various types of coatings can be applied to aluminum to provide additional protection and aesthetic appeal.
| Coating Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Coating | Dry powder is electrostatically applied and then cured under heat. | Durable and decorative finishes for automotive parts, appliances, and outdoor furniture. |
| Liquid Paint | Traditional liquid application, available in a wide range of colors. | Architectural components, aerospace parts, and marine equipment. |
| Ceramic Coating | Provides a high-temperature resistant finish with excellent durability. | Engine components, exhaust systems, and industrial machinery. |
| Epoxy Coating | Offers excellent chemical resistance and adhesion. | Protective coatings for industrial equipment, pipelines, and marine applications. |
5.3 Polishing and Finishing

Polishing and finishing techniques are employed to achieve the desired surface texture and appearance of aluminum parts.
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Polishing | Uses abrasives to smooth the surface, providing a mirror-like finish. | Enhances aesthetic appeal and provides a smooth, reflective surface. |
| Chemical Polishing | Involves the use of chemical baths to remove surface imperfections and enhance brightness. | Achieves a high-quality, bright finish with minimal mechanical effort. |
| Electro-Polishing | An electrochemical process that removes material and smooths the surface. | Provides a clean, smooth, and highly reflective finish. |
| Brushing | Involves using abrasive brushes to create a uniform, textured finish. | Produces a matte or satin finish that reduces glare and hides fingerprints. |
6. Tips for Choosing and Buying Custom Aluminum Parts
6.1 Factors to Consider
When selecting custom aluminum parts, it’s essential to evaluate several critical factors to ensure you get the best quality and value:
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Choose the appropriate aluminum grade based on the part’s application and requirements. | Ensures the part will perform well under specific conditions and meet industry standards. |
| Tolerance and Precision | Verify the precision and tolerance levels required for the part’s functionality. | Critical for parts that need to fit precisely within assemblies or meet strict performance criteria. |
| Surface Finish | Determine the necessary surface finish for aesthetic or functional purposes. | Affects both the appearance and durability of the part. |
| Quantity | Consider the production volume when selecting a supplier. | Some suppliers specialize in low-volume custom orders, while others are better for high-volume production. |
| Lead Time | Assess the turnaround time for production and delivery. | Ensures the parts will be available when needed to avoid project delays. |
| Cost | Compare costs from different suppliers, keeping in mind quality and additional services. | Helps in budgeting and ensures you get the best value for your money. |
6.2 Choosing the Right Supplier
Selecting a reliable supplier is crucial for obtaining high-quality custom aluminum parts. Here are some tips to help you choose the right supplier:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in aluminum fabrication. Experienced suppliers are more likely to understand your needs and provide quality products. Evaluate their portfolio and case studies to gauge their capability.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure the supplier has stringent quality control processes in place. This guarantees that the parts meet your specifications and standards. Look for certifications and industry standards compliance, such as ISO 9001, to ensure high-quality production.
- Customer Service: A supplier with excellent customer service will be responsive to your inquiries, provide detailed quotes, and offer support throughout the production process. Good communication is key to ensuring that your specifications are met accurately.
- Capabilities: Verify the supplier’s capabilities in terms of equipment, technology, and processes. Make sure they can handle your specific requirements, whether it involves CNC machining, extrusion, or casting. Advanced capabilities like CAD/CAM software usage can also be a significant advantage.
- Certifications: Check for industry certifications and compliance with relevant standards. This can be an indicator of the supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability. Certifications from organizations like the Aluminum Association or similar entities can provide additional assurance.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, fabricating aluminum parts involves various processes such as CNC machining, extrusion, casting, sheet metal fabrication, and 3D printing. Each method offers unique benefits and is suited for different applications. By understanding these techniques and considering factors like material grade, precision, and supplier reliability, you can ensure high-quality results for your projects.
If you’re looking for a trusted supplier, RALLY offers exceptional expertise and services in aluminum fabrication. Contact RALLY today to discuss your custom aluminum part needs and experience their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction firsthand.
Work with RALLY for CNC Machining Parts
Request a quote for new project today! No minimum order quantity and free samples available!







