Rapid Prototyping Services
Transform your ideas into reality quickly and efficiently with our tailored rapid prototyping solutions.
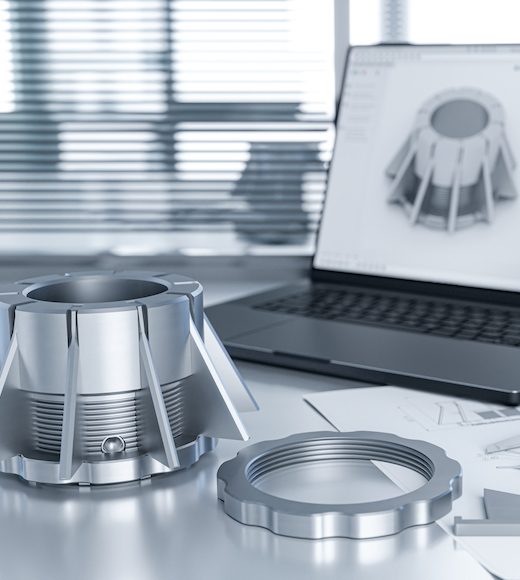

Rapid Prototyping Services
At RALLY, we are a leading provider of precision manufacturing solutions, specialising in rapid prototyping services to meet the needs of a wide range of industries. With years of experience in CNC machining and advanced manufacturing techniques, our team is dedicated to transforming your innovative ideas into high quality prototypes.
RALLY’s services have been recognised by a wide range of industries including aerospace, automotive, medical devices and more. Our clients highly value our professionalism and service quality and have established long-term relationships.
Our mission is to provide our clients with tailor-made solutions to accelerate product development and bring concepts to market faster.
Our Services
RALLY offers a range of services, including but not limited to:
CNC Machining Prototyping
RALLY’s CNC machining prototyping service delivers high precision and intricate designs, ensuring that every detail is captured accurately for a wide range of applications, from complex components to functional testing.
3D Printing Prototyping
The 3D printing prototyping service enables rapid production of complex geometries, ideal for visual presentations and functional testing. This service accelerates the development process, allowing for quick iterations and adjustments.
Low-Volume Production
Low-volume production options allow clients to test products in the market without committing to large-scale manufacturing. This flexibility helps validate designs and gather valuable feedback while minimizing risks.
Rapid Response Customer Support
RALLY provides rapid response customer support to assist clients throughout the project lifecycle. This ensures timely solutions and effective communication, helping to keep projects on track and meet deadlines efficiently.
RALLY's Advantages
No Minimum Order Quantity
Place flexible orders to meet small batch production needs, avoiding inventory buildup and adapting to various project scales.Custom Design According to Technical Drawings
Comprehensive customization services ensure products meet specific requirements, perfectly aligning with design concepts.Diverse Material Options
Choose from a variety of materials, including brass, aluminum, plastics, and metals, with the best material recommendations based on product needs.Fast Turnaround Time
Optimized production processes guarantee quick deliveries, meeting urgent project timelines.Free Samples Provided
Clients can request free samples to evaluate quality, ensuring satisfaction before committing to larger orders.
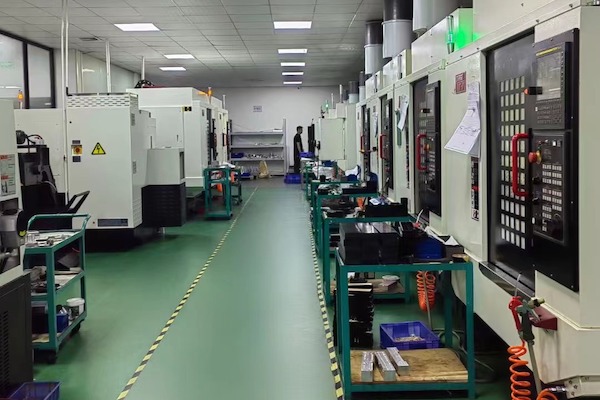

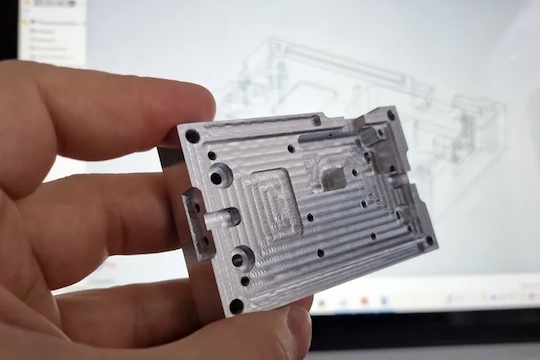
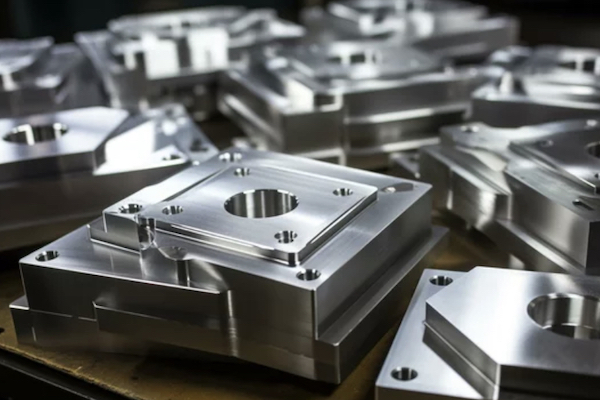
CNC Machining Prototype Service
RALLY provides exceptional CNC Machining Prototype Service, specializing in high-precision prototypes tailored to your specific design needs. Our advanced CNC machining technology ensures that every intricate detail is captured accurately, making it ideal for applications ranging from functional testing to production components. With a commitment to quality and speed, RALLY helps you transform your innovative ideas into tangible prototypes efficiently.
Partnering with RALLY means gaining access to expert support throughout the entire process. Our team is dedicated to understanding your unique requirements, ensuring that each prototype meets your specifications. With no minimum order quantities and rapid turnaround times, you can confidently test your designs in the market.
Reach out today to request a quote or learn more about how RALLY can help you achieve your project goals!


Get a Quick Quote for Free Samples
Request a quick quote now and receive free samples of our precision CNC machining parts tailored to your specifications!
FAQ for Rapid Prototyping
1. What materials can you use for rapid prototyping?
2. How do you ensure the quality of Rapid Prototyping?
3. What is the typical lead time for rapid prototyping?
4. What is the minimum order quantity for rapid prototyping?
5. What industries do you serve with your rapid prototyping services?
6. How can I request a quote for my project?
Get in Touch
Ready to get started? Contact us today for a free quote!
Metal Material
Aluminum, Brass, Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Copper, Titanium, etc.
Plastic Material
Acetal (Delrin), PTFE (Teflon), Acrylic (PMMA), PEEK, Nylon, ABS, PC, PP, POM, HDPE, PVC.
Surface Finishing
Anodizing, Powder Coating, Plating, Passivation, Bead Basting, Polishing, etc.
Inquiry Form
Let’s Start A New Project Today, Get Free Samples!
All You Need To Know About Rapid Prototyping
Table of Contents
What is rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a technique used to rapidly develop and validate product designs. It allows designers and engineers to quickly create physical models or prototypes to test and evaluate a product’s appearance, functionality and performance.
This technique is an integral part of modern product development, helping to iterate and improve faster based on real-world testing and user feedback. The benefits of rapid prototyping include shorter product development cycles, lower development costs, increased design flexibility and reduced risk.

What are the advantages of rapid prototyping?
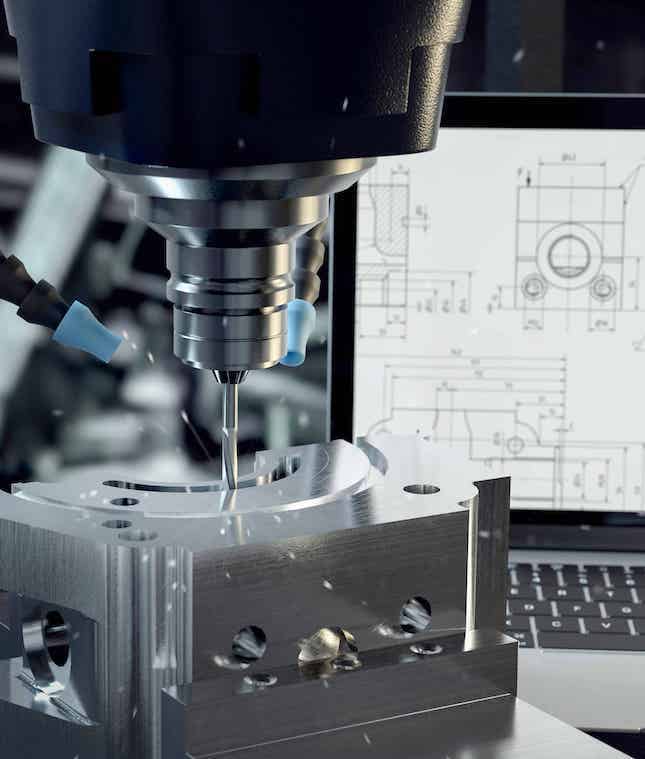

Reduced Development Time:
Rapid prototyping accelerates the design process, enabling quick verification and iteration, which shortens the overall product time to market significantly.
Cost Savings:
Early identification of design flaws minimizes expensive revisions during production, ultimately reducing overall development and manufacturing costs.
Enhanced Design Flexibility:
Prototyping allows for quick design iterations, adapting easily to market feedback and changing customer needs throughout the development process.
Improved Product Quality:
Testing prototypes ensures performance optimization before production, leading to higher quality and more reliable final products that meet customer expectations.
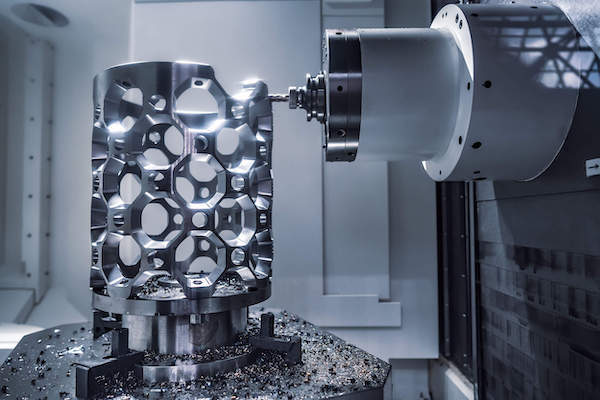
What are the rapid prototyping processes?
3D Printing:
This technology constructs complex-shaped parts by adding material layer by layer, offering flexibility and efficiency. It’s suitable for small batch production and customization, enabling rapid realization of design concepts and shortening product development cycles. It can use various materials like plastics, metals, and composites, widely applied in fields such as medical, aerospace, and automotive.
CNC Machining:
CNC machining utilizes computer-controlled machines to precisely remove excess material from solid blocks, producing high-precision parts. This process is suitable for various materials, including metals and plastics, and can achieve complex geometries. Its high efficiency and repeatability make it ideal for industrial production and prototyping, especially in aerospace and medical device sectors.
Laser Cutting:
Laser cutting technology employs high-energy laser beams to precisely cut complex shapes from flat materials, suitable for metals, plastics, and wood. It offers fast cutting speeds, high precision, and a small heat-affected zone, reducing the need for further processing. It’s widely used in manufacturing, advertising, and artistic creation, meeting diverse design needs.
Injection Molding:
Injection molding is a technique that injects molten plastic into molds to cool and form parts, ideal for large-scale production. It achieves high precision and complex shapes, widely used in consumer goods, automotive, and electronics. Although the initial mold cost is high, its unit cost significantly decreases in large production, making it an efficient manufacturing choice.
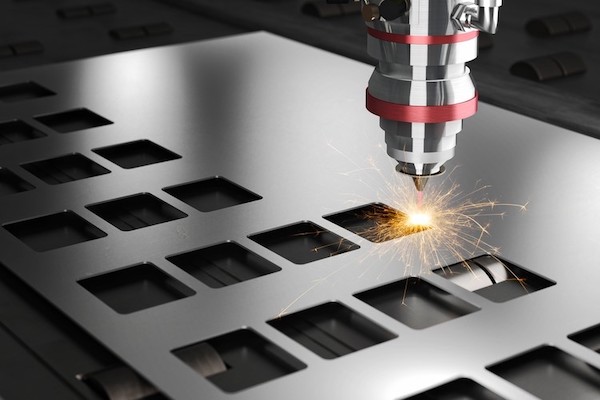




What are the applications of rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is widely used across various industries, including:
Rapid prototyping significantly accelerates the design process for electronic products. By creating prototypes, designers can test aesthetics and user experience early on, ensuring that the final product aligns with market demands.
This approach helps refine features and usability, leading to better consumer satisfaction and a more competitive product in the marketplace.
In the automotive industry, rapid prototyping is crucial for testing components before full-scale production. By creating prototypes, manufacturers can assess the performance and compatibility of parts, optimizing designs for safety and efficiency.
This iterative process reduces the risk of costly recalls and ensures that the final vehicles meet industry standards and consumer expectations.
Rapid prototyping plays a vital role in the development of medical devices by allowing engineers to create functional models for clinical testing. These prototypes help evaluate safety and effectiveness in real-world applications, facilitating necessary adjustments before final production.
This ensures compliance with regulatory standards and enhances patient safety, ultimately improving healthcare outcomes.
The aerospace industry benefits from rapid prototyping through the swift development and validation of aircraft components. Prototyping allows for rigorous testing to ensure that parts meet strict safety standards and performance requirements.
This process not only speeds up development but also enhances the reliability and safety of aerospace products, critical in this highly regulated industry.
In industrial manufacturing, rapid prototyping is essential for creating prototypes of tools, fixtures, and machine parts. This practice enhances production efficiency and accuracy by allowing manufacturers to identify design flaws early.
By reducing manufacturing time and costs, rapid prototyping leads to improved operational efficiency and higher-quality final products.
Is rapid prototyping the same as 3d printing?
Rapid prototyping and 3D printing are not the same, but 3D printing is a common technique used in rapid prototyping.
Definition:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a specific method of rapid prototyping. It builds three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer, typically based on computer-generated 3D models.
3D printing technology encompasses various specific methods, such as Stereolithography (SLA), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
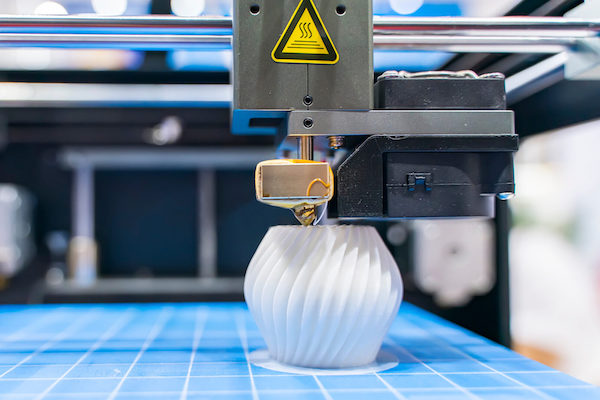

Rapid prototyping : refers to the process of quickly creating models or samples of products during the development phase using advanced manufacturing technologies. This process aims to help designers and engineers swiftly validate design concepts, test product functionality and performance, and gather user feedback. Rapid prototyping can employ various techniques, including but not limited to 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting.
Key Differences:
Technology Scope: Rapid prototyping is a broad concept that encompasses various manufacturing technologies, while 3D printing is a specific implementation within that framework.
Application Purpose: The primary goal of rapid prototyping is to accelerate the product development process by quickly building models to gather feedback and iterate, whereas 3D printing focuses on achieving this through additive manufacturing techniques.
Materials and Processes: Although 3D printing can be used for rapid prototyping, rapid prototyping can also employ other techniques (such as CNC machining) and materials that may not involve additive manufacturing.
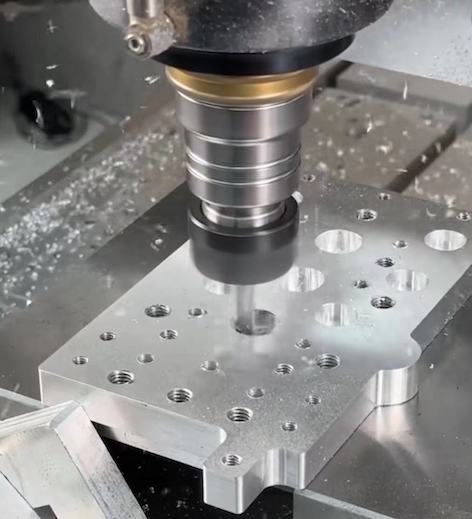

What are the common materials used in rapid prototyping?
Common materials used in rapid prototyping include:
PLA (Polylactic Acid) – A biodegradable plastic commonly used in 3D printing for its ease of use and good surface finish.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) – A durable plastic that offers good strength and impact resistance, suitable for functional prototypes.
Nylon – Known for its flexibility and strength, nylon is often used for prototypes that require durability and wear resistance.
Aluminum – A lightweight metal that is easy to machine, commonly used for precision prototypes in various applications.
Steel – Used for strong, high-stress components, steel prototypes offer excellent durability and performance.
Resin – Used in SLA (Stereolithography) 3D printing, resins can produce highly detailed prototypes with smooth finishes.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) – A versatile plastic used for various applications, offering good chemical resistance and durability.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) – A high-performance thermoplastic known for its strength and heat resistance, ideal for demanding applications.
How can rapid prototyping be extended to mass production?
Once the design is finalized, scaling up rapid prototyping to mass production involves several key steps:
1. Design for Manufacturability (DFM):
Review and optimize the design to ensure it can be efficiently produced at scale, considering factors like material choice and production methods.
2. Select Appropriate Manufacturing Methods:
Choose the right manufacturing processes that align with the design requirements and production volume, such as injection molding, CNC machining, or additive manufacturing.
3. Create Production Tools:
Develop necessary tooling and molds for the selected manufacturing method. This may include designing injection molds or machining fixtures.
4. Conduct Pilot Runs:
Execute pilot production runs to test the manufacturing process, identify any issues, and make necessary adjustments before full-scale production.
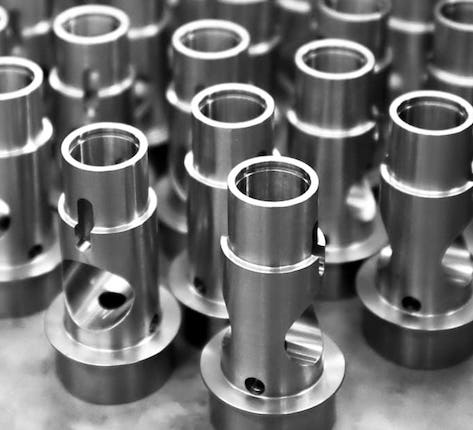

5. Implement Quality Control Processes:
Establish quality assurance protocols to ensure that the products meet specifications consistently during mass production.
6. Establish Supply Chain Logistics:
Organize the supply chain for materials and components, ensuring a reliable flow of resources to support ongoing production.
7. Monitor and Optimize Production:
Continuously monitor the production process and make improvements to increase efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance product quality.
Work with RALLY for Rapid Prototyping
Request a quote for new project today! No minimum order quantity and free samples available!
