Are you struggling to find a cost-effective solution for producing small quantities of high-precision parts? Frustrated with the limitations of traditional manufacturing methods? Small batch CNC machining might be the answer you’ve been searching for. This innovative approach combines the precision of CNC technology with the flexibility of producing smaller batches, allowing for rapid prototyping, custom designs, and reduced lead times.
Dive into our comprehensive guide on small batch CNC machining and discover how it can transform your manufacturing process, offering both efficiency and affordability.
1. What Is Small Batch CNC Machining?
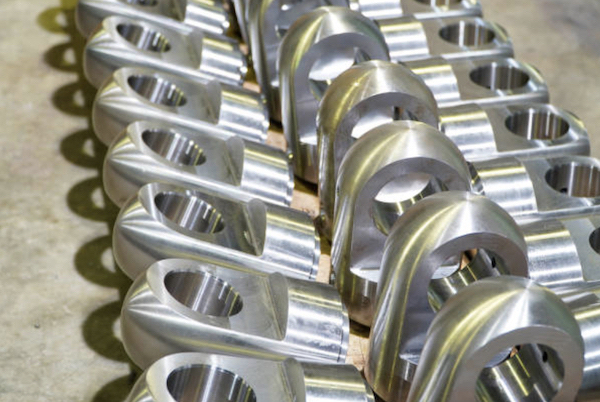

Small batch CNC machining is a game-changer for industries requiring precise, high-quality parts without committing to large-scale production. Imagine needing a small number of custom parts, but traditional manufacturing methods either require a massive order or charge exorbitantly for a small run. That’s where small batch CNC machining steps in.
This process leverages Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology to create intricate parts with incredible accuracy, even in limited quantities. Whether you’re in aerospace, automotive, or medical industries, this method offers unparalleled flexibility and efficiency.
By using small batch CNC machining, you can quickly prototype new designs, test various materials, and make modifications without the financial burden of mass production. It’s the perfect solution for startups, custom projects, or any situation where precision and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
Small batch CNC machining empowers you to innovate and bring your ideas to life faster and more affordably. So, if you’re looking to break free from the constraints of traditional manufacturing, small batch CNC machining might just be the solution you need to stay ahead in a competitive market.
2. How Does Small Batch Machining Work?

Have you ever been bogged down by the complexity and cost of producing small quantities of custom parts? Small batch machining is designed to solve exactly that problem, offering a streamlined, cost-effective solution that doesn’t compromise on quality or precision.
Small batch machining utilizes advanced Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology. This involves using computer-driven machines to produce parts with exceptional accuracy and repeatability. The process begins with designing the part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. Once the design is finalized, it’s converted into a machine-readable format known as G-code, which directs the CNC machine on how to create the part.
The beauty of small batch machining lies in its flexibility. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which requires expensive and time-consuming setups, small batch machining can quickly transition from one part to another with minimal downtime. This is perfect for projects that need a quick turnaround or for testing and prototyping new designs without committing to large-scale production runs.
Furthermore, small batch machining allows for precise control over the production process. You can experiment with different materials, test various finishes, and make iterative adjustments to the design with ease. This adaptability not only saves time but also significantly reduces costs, making it an ideal choice for startups, innovators, and businesses looking to stay agile and responsive to market demands.
In essence, small batch machining is all about bringing your creative visions to life with maximum efficiency and minimal waste. Whether you’re developing a new product, customizing components, or simply need a few high-quality parts, this process offers a seamless and scalable solution that keeps you ahead of the competition.
3. Types of Small Batch CNC Machining
Are you looking to produce high-quality parts in small quantities but unsure which machining process to choose? Understanding the different types of small batch CNC machining can help you select the best method for your specific needs, ensuring precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
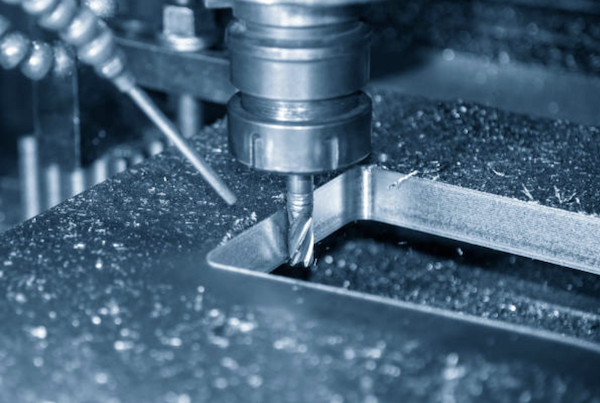

Milling
Milling is one of the most versatile and widely used CNC machining processes. It involves using rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece, creating intricate shapes and complex features. Whether you’re crafting prototypes, custom parts, or small production runs, CNC milling offers exceptional accuracy and flexibility. With capabilities to work on various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, milling is perfect for projects that demand high precision and intricate detailing.
Turning
Turning is another critical CNC machining process, ideal for creating cylindrical parts. This method uses a lathe to rotate the workpiece while a cutting tool shapes it. Turning is particularly effective for producing parts like shafts, bushings, and other round components. With CNC turning, you can achieve tight tolerances and smooth finishes, making it a preferred choice for automotive, aerospace, and medical industries where precision is paramount.
Drilling and Tapping
Drilling and tapping are essential processes for creating holes and threads in a workpiece. CNC drilling uses high-speed rotating drill bits to produce precise holes, while tapping forms internal threads within these holes. These processes are crucial for parts that require assembly with screws, bolts, or other fasteners. Small batch CNC drilling and tapping ensure that each hole and thread is consistently accurate, enhancing the overall quality and reliability of the final product.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a unique CNC process used for hard metals or materials that are difficult to machine with traditional methods. EDM works by creating sparks that erode material from the workpiece. This method is perfect for creating intricate shapes, fine details, and complex geometries that would be challenging with other machining techniques. Small batch EDM is often employed in the aerospace, automotive, and tool-making industries for producing precision components.
Laser Cutting and Engraving
Laser cutting and engraving are advanced CNC processes that use focused laser beams to cut or engrave materials. These methods are known for their high precision, speed, and ability to work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. Laser cutting is ideal for producing detailed parts with clean edges, while laser engraving adds custom markings or designs to the surface of a workpiece. For small batch production, laser processes offer unmatched accuracy and customization options.
By understanding the various types of small batch CNC machining, you can choose the most suitable method for your project’s requirements. Each process offers unique advantages, enabling you to achieve the desired level of precision, detail, and efficiency. Embrace the versatility of small batch CNC machining to bring your innovative designs to life with exceptional quality and consistency.

4. Small Batch CNC Machining Materials
Choosing the right materials for your small batch CNC machining projects can significantly impact the quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness of your parts. Whether you’re developing prototypes, custom components, or low-volume production runs, understanding the characteristics and benefits of various materials is crucial. Let’s explore the most commonly used materials in small batch CNC machining: metals, plastics, and composites.
1. Metals
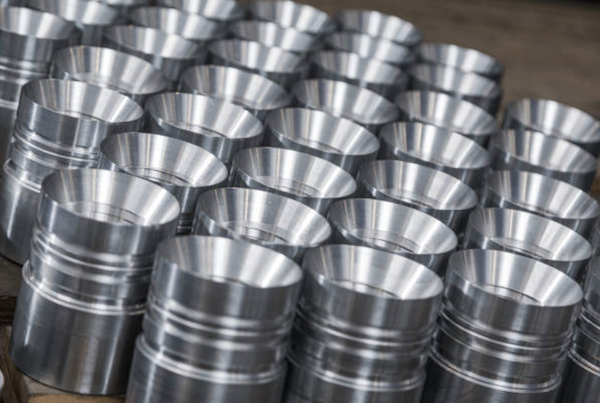

Metals are a staple in CNC machining due to their strength, durability, and versatility. They are ideal for applications that demand high precision and robust performance. Here are some popular metals used in small batch CNC machining:
Aluminum: Known for its lightweight and excellent machinability, aluminum is perfect for prototypes and components requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio. It’s widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
Steel: Offering exceptional strength and durability, steel is a go-to material for parts that need to withstand high stress and wear. Stainless steel, in particular, is favored for its corrosion resistance, making it suitable for medical devices, food processing equipment, and outdoor applications.
Brass: This metal is prized for its machinability, low friction, and aesthetic appeal. Brass is commonly used in applications requiring intricate detailing, such as gears, valves, and decorative hardware.
Titanium: Renowned for its high strength, low weight, and excellent corrosion resistance, titanium is ideal for aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance automotive components. Despite its higher cost, titanium’s superior properties make it a valuable choice for critical applications.
2. Plastics
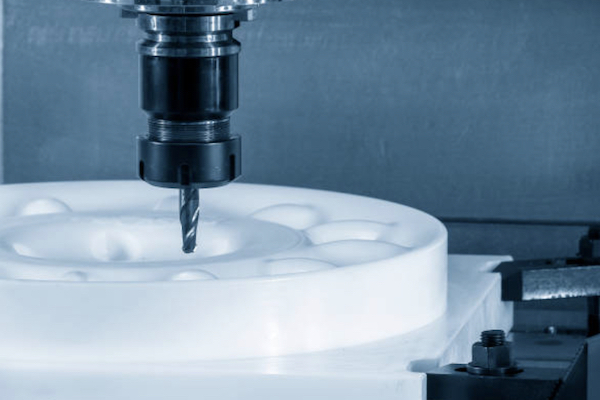

Plastics offer a unique combination of flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and versatility, making them an excellent choice for various CNC machining projects. They are especially useful for parts that require electrical insulation, chemical resistance, or lightweight properties. Here are some commonly used plastics in small batch CNC machining:
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is a tough, impact-resistant plastic that’s easy to machine. It’s widely used for enclosures, housings, and consumer products due to its durability and affordability.
Polycarbonate: Known for its transparency and high impact resistance, polycarbonate is ideal for applications like safety equipment, lenses, and transparent covers. It’s also resistant to heat and UV light.
Nylon: This versatile plastic is known for its strength, toughness, and wear resistance. Nylon is commonly used for mechanical parts such as gears, bushings, and bearings due to its excellent mechanical properties.
POM (Polyoxymethylene): Also known as Delrin, POM is a highly crystalline plastic that offers low friction, high stiffness, and dimensional stability. It’s perfect for precision parts like gears, pulleys, and medical devices.
3. Composites
Composites are engineered materials made from two or more constituent materials with different physical or chemical properties. The combination results in a material that has superior properties compared to the individual components. Composites are highly valued in industries that require high strength-to-weight ratios, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Here are some examples:
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP): Known for its exceptional strength and low weight, CFRP is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment. It offers excellent fatigue resistance and can be molded into complex shapes.
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP): Also known as fiberglass, GFRP is strong, lightweight, and cost-effective. It’s commonly used in construction, marine, and consumer goods industries. Fiberglass parts are resistant to corrosion and can withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Kevlar Reinforced Composites: Kevlar is renowned for its high tensile strength and impact resistance. Composites reinforced with Kevlar are used in applications requiring extreme durability, such as body armor, high-performance sporting goods, and aerospace components.
5. Types of Small Batch CNC Machining Finishes
Selecting the right finish for your CNC machined parts can significantly enhance their performance, aesthetics, and durability. Different finishes offer various benefits, from improved corrosion resistance to enhanced appearance, making them an essential part of the manufacturing process. Let’s explore the most common types of small batch CNC machining finishes and how they can add value to your projects.
Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the surface of metal parts, typically aluminum, into a durable, corrosion-resistant, and aesthetically pleasing oxide layer. This finish is particularly popular for its ability to improve wear resistance, enhance surface hardness, and offer a variety of color options.
Benefits: Anodizing provides excellent protection against corrosion and wear, increases the surface hardness, and allows for vibrant and durable coloring options. It’s ideal for parts exposed to harsh environments or requiring a high level of aesthetic appeal.
Applications: Commonly used in aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, and architectural components where both performance and appearance are critical.
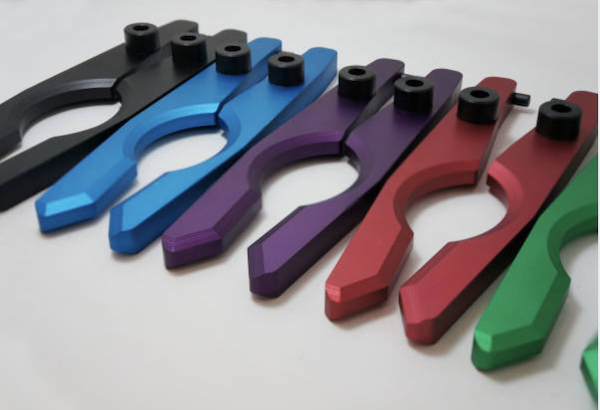

Powder Coating
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the surface of a part, which is then cured under heat to form a solid, durable coating. This finish is known for its robustness, vibrant colors, and ability to create a thicker coating than traditional liquid paints.
Benefits: Powder coating offers superior durability, resistance to chipping, scratching, and fading, and provides a uniform and attractive finish. It is also environmentally friendly, as it emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to liquid coatings.
Applications: Widely used in automotive parts, household appliances, outdoor furniture, and industrial equipment, where a tough, long-lasting finish is required.
Polishing and Plating
Polishing and plating are finishing processes that enhance the appearance and surface properties of machined parts. Polishing involves mechanically or chemically smoothing the surface to achieve a mirror-like finish, while plating involves coating the part with a thin layer of metal, such as nickel, chrome, or gold.
Benefits: Polishing improves the aesthetic appeal by creating a smooth, shiny surface, while plating adds a protective layer that can improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Common in jewelry, automotive trim, electronic components, and medical devices where a high-quality surface finish and additional protective properties are desired.
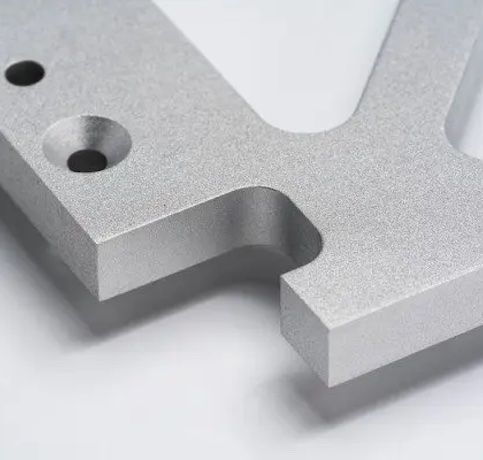

Sandblasting
Sandblasting, or abrasive blasting, is a finishing process that involves propelling abrasive particles against a part’s surface to clean, roughen, or smooth it. This process is excellent for removing surface contaminants, creating a uniform texture, and preparing the part for further finishing.
Benefits: Sandblasting can improve paint adhesion, remove surface impurities, and create a consistent texture. It also allows for various levels of surface roughness, depending on the abrasive material and blasting intensity used.
Applications: Often used in preparing parts for painting or coating, cleaning rusty or contaminated surfaces, and creating decorative textures on metal, glass, or plastic parts.
Passivation
Passivation is a chemical process used to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel parts. It involves treating the surface with an acid solution to remove free iron and other contaminants, resulting in the formation of a passive oxide layer that protects against rust and corrosion.
Benefits: Passivation significantly improves the corrosion resistance of stainless steel, extends the life of the parts, and ensures a clean, contamination-free surface.
Applications: Ideal for medical instruments, food processing equipment, aerospace components, and any application where corrosion resistance and cleanliness are crucial.
Black Oxide Coating
Black oxide coating is a conversion coating for ferrous materials, providing a matte black finish that enhances corrosion resistance and reduces light reflection. This finish is created through a chemical reaction between the metal surface and an oxidizing agent.
Benefits: Black oxide coating offers moderate corrosion protection, improves wear resistance, and reduces glare. It also enhances the aesthetic appeal with a uniform black finish.
Applications: Commonly used in firearms, tools, automotive parts, and industrial machinery where both functional and decorative qualities are important.
6. Advantages of Small Batch CNC Machining
Are you looking for a manufacturing solution that combines precision, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness? Small batch CNC machining might be exactly what you need. This innovative approach offers numerous advantages that can significantly enhance your production process, especially when dealing with custom parts or limited quantities. Let’s explore the key benefits of small batch CNC machining and how it can help your business thrive.
Flexibility and Customization
One of the standout advantages of small batch CNC machining is its unparalleled flexibility. Whether you’re working on prototypes, custom parts, or specialized components, this method allows you to easily adapt and modify designs without the constraints of large-scale production.
Rapid Prototyping: Small batch CNC machining is perfect for rapid prototyping, enabling you to quickly produce and test new designs. This flexibility accelerates the development process, allowing for faster iterations and refinements based on feedback and testing results.
Customization: With small batch CNC machining, you can produce highly customized parts tailored to specific needs and applications. This is particularly beneficial for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where unique and precise components are often required.
Cost-Efficiency for Prototypes and Low-Volume Production
Producing small quantities of parts using traditional manufacturing methods can be prohibitively expensive due to high setup costs and minimum order requirements. Small batch CNC machining offers a cost-effective alternative that can save you both time and money.
Reduced Setup Costs: Traditional manufacturing often involves significant setup costs, which are spread across large production runs. In contrast, small batch CNC machining minimizes these costs, making it more economical for low-volume production and prototypes.
Lower Inventory Costs: By producing only what you need, when you need it, you can avoid the costs associated with maintaining large inventories. This approach not only reduces storage expenses but also minimizes the risk of obsolete or excess inventory.
Quick Turnaround Times
Time is a critical factor in any manufacturing process, and small batch CNC machining excels in delivering quick turnaround times. This is essential for meeting tight deadlines and staying competitive in fast-paced markets.
Efficient Production: CNC machines are highly automated and capable of running continuously with minimal supervision. This efficiency translates to faster production times, allowing you to meet deadlines and reduce lead times.
Rapid Adjustments: The ability to quickly adjust and fine-tune the machining process ensures that any issues or design changes can be addressed promptly. This agility helps you maintain a smooth production flow and respond swiftly to market demands.
High Precision and Consistency
Precision is a hallmark of CNC machining, and small batch production is no exception. The technology ensures that each part is manufactured to exact specifications, maintaining high quality and consistency throughout the production run.
Tight Tolerances: CNC machines are capable of achieving extremely tight tolerances, which is crucial for parts that require high precision. This level of accuracy is essential for applications in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and electronics.
Consistency: The automated nature of CNC machining ensures that each part produced is consistent in quality and dimensions. This repeatability is vital for maintaining product standards and ensuring compatibility across different components.
Material Versatility
Small batch CNC machining supports a wide range of materials, giving you the flexibility to choose the best material for your specific application. This versatility is essential for optimizing the performance and durability of your parts.
Metals: From aluminum and steel to titanium and brass, CNC machining can handle a variety of metals with ease. This makes it suitable for producing strong, durable parts for demanding applications.
Plastics: CNC machining is also adept at working with various plastics, including ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon. These materials are ideal for parts that require lightweight properties, electrical insulation, or chemical resistance.
Composites: For applications that demand high strength-to-weight ratios, CNC machining can process composite materials like carbon fiber and fiberglass. These materials are often used in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment.
Enhanced Surface Finishes
The surface finish of a part can significantly impact its performance, aesthetics, and usability. Small batch CNC machining offers a variety of finishing options to meet your specific requirements.
Surface Smoothness: CNC machining can achieve high-quality surface finishes, reducing the need for additional post-processing. This smoothness is essential for parts that require tight fits or are used in high-visibility applications.
Finishing Processes: Additional finishing processes such as anodizing, powder coating, and polishing can further enhance the appearance and durability of your parts. These finishes provide added protection against corrosion, wear, and environmental factors.
By leveraging the advantages of small batch CNC machining, you can enhance your production capabilities, reduce costs, and deliver high-quality parts that meet the exact needs of your customers. Whether you’re a startup, an established manufacturer, or a custom parts provider, this approach offers the flexibility and efficiency required to succeed in today’s competitive market. Embrace small batch CNC machining to unlock new possibilities and drive innovation in your manufacturing process.
7. What Is the Cost Aspect of Small Batch Machining?
When it comes to manufacturing, cost is a critical factor that can influence decision-making, especially for small batch production. Understanding the cost aspects of small batch CNC machining can help you make informed decisions, optimize your budget, and achieve the best value for your investment. Let’s delve into the factors affecting costs and how small batch machining compares with other manufacturing methods.
1. Factors Affecting Costs
Several factors can influence the cost of small batch CNC machining, each contributing to the overall expense of the project. By understanding these factors, you can better manage your budget and make cost-effective choices.
Material Costs: The type and quality of materials used significantly impact the cost. Metals like titanium and stainless steel tend to be more expensive than aluminum or plastic. Additionally, the amount of material required for the batch also plays a role in determining the total cost.
Complexity of Design: More intricate and complex designs require longer machining times and specialized tools, increasing the overall cost. Simple parts with straightforward geometries are typically less expensive to produce.
Tolerance and Precision Requirements: Tight tolerances and high precision add to the machining cost. Achieving these requires advanced machinery, skilled labor, and more time, all of which contribute to higher expenses.
Setup Costs: Even for small batch production, there are initial setup costs involved, including programming the CNC machine, creating jigs or fixtures, and preparing the materials. While these costs are relatively fixed, they can be spread over a larger number of parts in larger batches, making them a more significant factor in small batch machining.
Labor Costs: Skilled labor is required to operate CNC machines, ensure quality control, and perform any necessary finishing processes. Labor costs can vary depending on the complexity of the project and the expertise required.
Finishing Processes: Additional finishing processes such as anodizing, powder coating, or polishing can add to the overall cost. These processes enhance the appearance and functionality of the parts but also involve extra time and materials.
Volume of Production: The number of parts being produced in a batch affects the cost per unit. While small batch production is inherently more expensive per unit compared to mass production, it can be more cost-effective for limited quantities where large-scale production is not feasible.
2. Comparing Costs with Other Manufacturing Methods
When evaluating the cost-effectiveness of small batch CNC machining, it’s essential to compare it with other manufacturing methods. Each method has its own set of advantages and cost implications, making some more suitable for certain applications than others.
Injection Molding: Injection molding is highly cost-effective for large-scale production due to its low per-unit cost once the molds are created. However, the initial cost of mold fabrication is high, making it less suitable for small batch production. CNC machining, on the other hand, has lower setup costs and is more flexible for producing small quantities.
3D Printing: 3D printing is excellent for rapid prototyping and complex geometries. It has low setup costs and is highly flexible for small batch production. However, CNC machining often provides better material properties, surface finishes, and dimensional accuracy, making it preferable for end-use parts that require high precision and durability.
Traditional Machining: Traditional machining methods, such as manual milling or turning, can be cost-effective for very low-volume production and simple parts. However, they lack the efficiency, precision, and repeatability of CNC machining. CNC machining is more suitable for complex parts and larger small batches.
Die Casting: Die casting is efficient for producing metal parts in high volumes, similar to injection molding. The cost of creating dies is high, making it impractical for small batch production. CNC machining offers greater flexibility and lower initial costs, making it more suitable for small batches.
Sheet Metal Fabrication: Sheet metal fabrication is ideal for parts with simple geometries and large, flat surfaces. While it can be cost-effective for small batches, CNC machining provides better precision and is suitable for more complex shapes and detailed features.
8. Small Batch CNC Machining In Different Industries
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, precision and reliability are non-negotiable. Components must meet stringent standards to ensure safety and performance. Small batch CNC machining excels in producing high-precision parts with tight tolerances, which is crucial for aerospace applications.
Prototyping and Testing: The aerospace sector frequently requires prototypes for testing new designs. Small batch CNC machining enables rapid prototyping, allowing engineers to quickly test and iterate designs, leading to faster innovation and development cycles.
Custom Components: Many aerospace applications involve custom parts tailored to specific functions. Small batch CNC machining provides the flexibility to produce these specialized components without the need for large production runs, making it cost-effective for unique or low-volume requirements.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is characterized by constant innovation and a demand for high-quality, reliable parts. Small batch CNC machining supports this by offering the ability to produce complex, custom parts efficiently.
Aftermarket Parts: For custom and performance vehicles, small batch CNC machining is ideal for creating aftermarket parts. This includes custom engine components, suspension parts, and interior accessories, allowing car enthusiasts to personalize their vehicles with precision-engineered components.
Prototyping New Models: Automotive manufacturers use small batch CNC machining to prototype new parts and assemblies during the development of new vehicle models. This allows for rigorous testing and validation before committing to mass production.
Medical Devices
The medical device industry relies on precision and compliance with strict regulatory standards. Small batch CNC machining offers the precision and consistency needed to produce high-quality medical components.
Custom Implants: Small batch CNC machining is essential for creating custom implants tailored to individual patients. This includes orthopedic implants, dental prosthetics, and surgical instruments, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal functionality.
Prototyping and Development: Medical device manufacturers use small batch CNC machining to develop and test new products. This process allows for rapid iteration and refinement, ensuring devices meet regulatory standards and perform as intended.
Electronics Industry
In the fast-paced electronics industry, innovation and precision are key. Small batch CNC machining provides the flexibility to produce intricate and precise components essential for electronic devices.
Enclosures and Housings: Electronics often require custom enclosures and housings to protect delicate components. Small batch CNC machining can produce these parts with high precision, ensuring proper fit and protection.
Prototyping Circuit Boards: Developing new electronic devices involves prototyping circuit boards and other components. Small batch CNC machining allows for quick production and testing of these prototypes, accelerating the development process.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation systems demand high-precision components to ensure reliable and efficient operation. Small batch CNC machining is perfectly suited to meet these requirements.
Custom Robotic Parts: Robotics applications often require custom parts, such as brackets, mounts, and sensor housings. Small batch CNC machining can produce these components with the necessary precision and durability.
Prototyping New Designs: Robotics engineers use small batch CNC machining to prototype new parts and mechanisms. This enables rapid testing and iteration, leading to faster development of innovative robotic solutions.
Consumer Products
The consumer products industry benefits from the ability to produce custom, high-quality parts in small quantities. Small batch CNC machining supports this need by offering flexibility and precision.
Customized Products: Small batch CNC machining allows for the production of customized consumer products, such as personalized jewelry, custom phone cases, and bespoke home decor items. This level of customization enhances customer satisfaction and adds value to the products.
Rapid Prototyping: Developing new consumer products involves prototyping and testing. Small batch CNC machining enables rapid production of prototypes, allowing designers to refine their ideas and bring new products to market quickly.
Industrial Equipment
The industrial equipment sector often requires robust and precise components to ensure the reliability and efficiency of machinery. Small batch CNC machining provides the necessary precision and flexibility for producing these parts.
Replacement Parts: Industrial equipment frequently needs custom replacement parts. Small batch CNC machining can produce these parts quickly and accurately, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
Custom Tooling: Manufacturing processes often require custom tooling. Small batch CNC machining allows for the production of specialized tools and fixtures tailored to specific manufacturing needs.
9. Alternatives to Small Batch CNC Machining
While small batch CNC machining offers numerous advantages, it’s not the only solution for producing high-quality parts in limited quantities. Depending on your project’s specific requirements, other manufacturing methods might be more suitable. Let’s explore three popular alternatives to small batch CNC machining: 3D printing, injection molding, and traditional machining.
1. 3D Printing
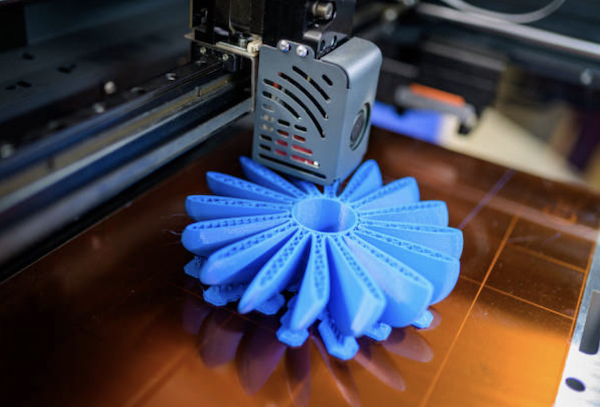

3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that creates parts layer by layer from digital models. This method has gained immense popularity due to its flexibility, speed, and ability to produce complex geometries.
Flexibility and Complexity: One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is its ability to produce intricate and complex designs that would be challenging or impossible with traditional machining. This makes it ideal for creating custom parts, prototypes, and intricate designs without the need for expensive tooling.
Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing excels in rapid prototyping, allowing designers to quickly produce and test multiple iterations of a part. This speeds up the development process and enables more efficient design validation and refinement.
Material Variety: While traditionally associated with plastics, 3D printing now supports a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, and composites. This expands its applications across various industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical devices and consumer products.
Cost-Effectiveness: For small quantities, 3D printing can be more cost-effective than CNC machining due to the elimination of setup costs and minimal material waste. However, it may not be as cost-effective for larger production runs due to slower production speeds and higher per-unit costs.
2. Injection Molding
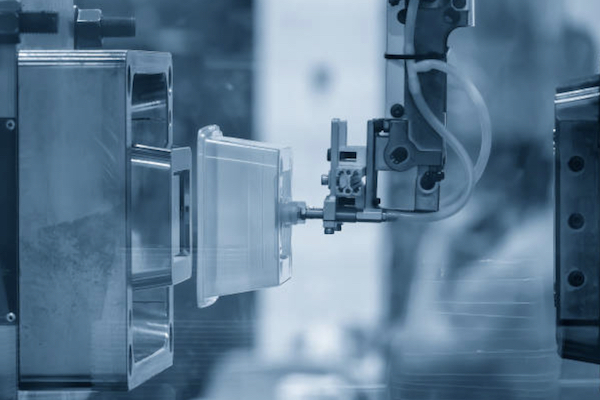
Injection molding is a well-established manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create parts. It is widely used for producing large volumes of plastic components with high precision and repeatability.
High Volume Efficiency: Injection molding is highly efficient for large-scale production, offering low per-unit costs once the molds are created. This makes it an excellent choice for manufacturing thousands or millions of identical parts.
High Precision and Quality: Injection molding provides excellent part consistency, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy. It is ideal for producing parts that require tight tolerances and high-quality finishes.
Material Versatility: Injection molding supports a wide range of materials, including various plastics, elastomers, and some metals. This versatility allows for the production of parts with different mechanical and thermal properties.
Upfront Tooling Costs: One of the main drawbacks of injection molding is the high initial cost of creating molds. For small batch production, this upfront investment can be prohibitive. However, for larger quantities, the cost per part decreases significantly, making it more economical.
3. Traditional Machining
Traditional machining encompasses a variety of manual and semi-automated processes, such as milling, turning, and drilling. These methods have been used for decades to produce parts from various materials.
Versatility: Traditional machining is highly versatile and can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. It is suitable for producing parts with different shapes, sizes, and complexity.
Low Setup Costs: Compared to CNC machining and injection molding, traditional machining typically has lower setup costs. This makes it a viable option for very low-volume production or one-off custom parts.
Skilled Labor: Traditional machining relies heavily on skilled operators to achieve precision and quality. While this can be an advantage for custom or complex parts, it also means that labor costs can be higher and consistency can vary based on operator skill.
Manual Processes: The manual nature of traditional machining can result in longer production times and lower efficiency compared to automated methods like CNC machining or injection molding. However, it remains a valuable option for projects that require a high degree of craftsmanship and flexibility.
Choosing the Right Method
When selecting the best manufacturing method for your project, consider the following factors:
Production Volume: For large-scale production, injection molding offers the best cost-efficiency. For low to medium volumes, CNC machining and 3D printing may be more suitable.
Design Complexity: 3D printing excels in producing complex geometries and custom designs. Traditional machining and CNC machining are better suited for parts with simpler geometries.
Material Requirements: Consider the material properties required for your part. 3D printing offers a growing range of materials, but CNC machining and traditional machining still provide the broadest material options.
Lead Time: If you need parts quickly, 3D printing and CNC machining offer faster turnaround times for prototypes and small batches compared to injection molding.
Budget: Evaluate your budget for tooling, setup, and production costs. 3D printing and CNC machining have lower upfront costs, while injection molding can be more cost-effective for large quantities.
10. How To Choose The Best Small Batch CNC Machining Services China Provider?
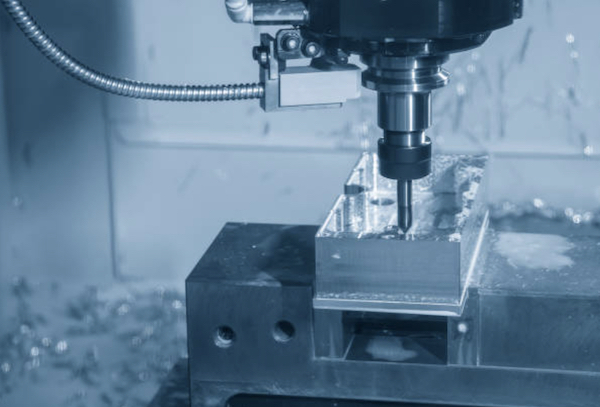
Selecting the best small batch CNC machining services provider in China can be a transformative decision for your business. To make an informed choice, consider using the RALLY method—Reputation, Advanced Capabilities, Lead Times, Logistics, and Your Specific Needs.
Reputation: Start by researching the provider’s industry reputation. Look for customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies that highlight their reliability and quality of service. A well-regarded provider will have a proven track record of delivering high-quality parts consistently.
Advanced Capabilities: Evaluate the technical capabilities of the provider. Ensure they use state-of-the-art CNC machines and have expertise in working with a variety of materials. Advanced capabilities also include offering comprehensive services such as milling, turning, drilling, and finishing.
Lead Times: Assess the provider’s ability to meet your deadlines. Quick and reliable turnaround times are crucial for keeping your projects on schedule. Providers that offer efficient production processes and responsive communication will help ensure timely delivery of your parts.
Logistics: Efficient logistics and shipping are vital for international partnerships. Choose a provider experienced in handling customs and import procedures, with reliable shipping options to ensure your parts arrive safely and on time.
Your Specific Needs: Finally, ensure the provider can tailor their services to meet your specific requirements. This includes offering customized solutions, scalable production, and excellent customer support to address any issues promptly.
By following the RALLY method, you can confidently select a small batch CNC machining provider in China that aligns with your business goals and delivers exceptional results.
Conclusion
Ready to improve the accuracy and efficiency of your manufacturing process? Learn about the benefits of working with the top small batch CNC machining supplier in China. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and learn how our expertise can bring your designs to life.
Work with RALLY for CNC Machining Parts
Request a quote for new project today! No minimum order quantity and free samples available!







