Introduction:
Are you a product engineer, designer, or project manager seeking to refine your product before full-scale manufacturing? At RALLY, we specialize in small-scale production to support you during the crucial prototype phase. Our precision CNC machining services ensure cost-effective, high-quality prototypes that allow you to validate designs, conduct testing, and make adjustments before committing to mass production. Whether you’re refining functionality or evaluating material performance, we offer tailored solutions to meet your needs. Let us help bridge the gap between concept and commercialization with reliable small-batch manufacturing.
Key Takeaways:
- Small-scale production reduces risks by validating product designs.
- Prototyping ensures product quality and identifies early design flaws.
- Small-batch manufacturing offers flexibility for testing and design adjustments.
- Smooth transition planning is essential from prototype to mass production.
1. What is a Prototype?
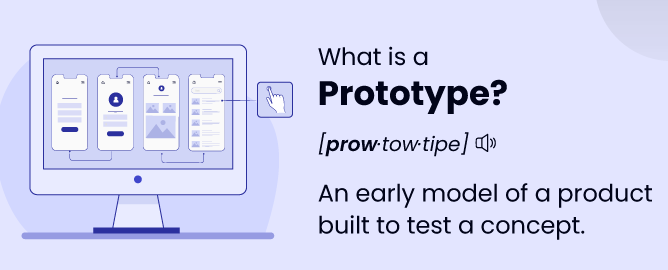
A prototype is an early sample or model of a product, built to test and validate its design, functionality, and feasibility. It serves as a tangible representation of an idea, allowing engineers, designers, and stakeholders to evaluate and refine the concept before moving to large-scale production.
Prototypes help identify potential flaws, explore material choices, and assess product performance. Depending on the stage of development, prototypes can range from simple mock-ups to fully functional versions. This iterative process ensures that the final product aligns with design goals and customer expectations, minimizing risks during mass production.
2. The Role of Prototypes in Product Development
Prototypes play a crucial role in product development by enabling teams to test, validate, and refine product designs before moving to mass production. They help identify design flaws, assess functionality, and explore material options early in the process.
By providing a physical representation of the product, prototypes allow for hands-on testing and stakeholder feedback, ensuring the final product meets performance expectations.
They also support iterative improvements, reducing risks and development costs. Prototypes are used at various stages, from concept validation to pre-production testing, bridging the gap between initial ideas and market-ready products.
3. Production Requirements During the Prototype Phase
The prototype phase demands specific production requirements to ensure the product’s design and functionality are thoroughly validated. Small-batch production is often preferred, providing flexibility to test different designs without committing to large quantities. High precision is essential to ensure components meet exact specifications, as even minor errors can affect performance during testing. Flexibility in production processes is also critical, allowing for quick adjustments based on feedback.
Choosing the right materials is crucial—some prototypes require alternatives to final materials to reduce costs, while others use production-grade materials for realistic testing. Ultimately, efficient production during this phase ensures a smooth transition from concept to full-scale manufacturing.
4. Why is Small-Scale Production Critical During the Prototype Phase?
Small-scale production plays a vital role in the prototype phase by minimizing risks and streamlining the product development process. It offers cost-efficiency, allowing companies to test designs without the high expense of mass production. This approach helps identify flaws and optimize designs early, reducing costly revisions later.
Additionally, small-scale production shortens the development cycle by enabling rapid testing and iteration. Quick feedback loops allow engineers and designers to refine products faster. The flexibility to make design adjustments during production is another key advantage, ensuring prototypes evolve with insights gathered from testing.
Ultimately, small-scale production ensures smoother transitions to mass production by validating both product performance and design feasibility.
Get Your CNC Parts Into Production Today
Your Global Partner for Quality CNC Machining Services in China!
5. How Does Small-Scale Production Fit into the Product Development Process?
Small-scale production is seamlessly integrated into multiple stages of the product development process, acting as a bridge between concept validation and mass manufacturing. Early in development, it supports concept validation by turning ideas into tangible prototypes that can be tested for functionality and design. As the design evolves, small-batch production facilitates iterative improvements, allowing teams to refine components based on real-world feedback.
During the pilot stage, small-scale production helps simulate full production processes, ensuring materials, tools, and workflows are optimized before scaling up. It also enables testing for compliance with industry standards and customer expectations. By gradually increasing production volumes, businesses can confidently transition to mass manufacturing with reduced risks and smoother operations.
6. Optimizing the Manufacturing Process for Small-Scale Production
Implement Lean Manufacturing:
Focus on reducing waste, streamlining workflows, and maximizing efficiency without compromising product quality.Utilize Flexible Production Planning:
Adapt quickly to design changes and evolving product requirements by maintaining flexible schedules and workflows.Leverage Automation and CNC Technology:
Automate repetitive tasks with CNC machining to increase precision, reduce human errors, and shorten production cycles.Use Multi-Purpose Machinery:
Employ versatile equipment to minimize setup time and lower costs by handling multiple tasks within a single machine.Establish Rigorous Quality Control Processes:
Apply strict quality checks to ensure that small production batches meet specifications, preventing defects before scaling up.
7. Scaling from Small-Scale Production to Mass Production
Gradual Volume Increases
Scale production incrementally to identify potential bottlenecks, refine processes, and ensure product consistency before full-scale manufacturing.Supply Chain Optimization
Secure reliable suppliers and ensure material availability to avoid disruptions. Establish contingency plans to manage risks in the supply chain.Equipment Upgrades and Capacity Planning
Assess current equipment capabilities and invest in new machinery or automation if needed to handle higher production volumes efficiently.Workforce Training and Expansion
Train existing staff to handle new processes and hire additional workforce as needed to support increased production demands.Quality Control Adaptation
Maintain rigorous quality control processes during the transition to ensure that product standards remain consistent, even as volumes increase.
8. Key Steps from Prototype to Production
Design Validation
Ensure the prototype meets all design requirements through functional testing, performance checks, and industry-standard compliance. Gather feedback from stakeholders and make necessary adjustments.Pilot Production
Conduct a small production run to validate the manufacturing process. Check equipment, tools, and materials, and identify any production issues. Ensure suppliers and logistics are ready for scaling up.Iteration and Optimization
Refine the product or process based on pilot production feedback. Establish quality control checkpoints, streamline production steps, and prepare detailed manufacturing documentation.Pre-Production Run
Perform a final small batch run using actual materials and conditions. Verify all adjustments, train staff on processes, finalize quality assurance protocols, and confirm packaging and logistics readiness.Full-Scale Production Launch
Begin mass production while continuously monitoring product quality, process efficiency, and supply chain performance. Collect post-launch feedback for ongoing improvements to meet customer expectations.
Get Your CNC Parts Into Production Today
Your Global Partner for Quality CNC Machining Services in China!
9. Evaluating the Final Prototype and Design Validation
Assessing the final prototype’s functionality, performance, and appearance is essential before moving to mass production. Functionality tests confirm that the prototype operates as intended, while performance assessments ensure it meets industry standards and customer expectations under various conditions.
The product’s appearance is also evaluated to align with design aesthetics, branding, and usability. A thorough evaluation minimizes the risk of flaws during large-scale manufacturing.
Design validation and iterative improvements play a critical role in refining the product. Feedback from prototype testing informs necessary adjustments, ensuring the product evolves to meet market needs.
Each iteration allows for fine-tuning, improving both function and design. By validating the prototype through multiple test cycles, businesses can achieve an optimal product that performs reliably, looks appealing, and is ready for seamless transition to mass production.
10. Managing Small-Scale Production
Effectively managing small-scale production requires balancing time, cost, and resources. Clear scheduling ensures production timelines align with development goals, avoiding delays.
Cost control is crucial, as small-batch production can be expensive per unit; optimizing material usage and minimizing waste helps manage expenses. Proper resource allocation, including skilled labor and specialized equipment, ensures smooth operations without interruptions.
To maintain smooth operations across all phases of product development, communication between design, engineering, and production teams is essential. Continuous monitoring allows early detection of potential issues, ensuring quick resolutions.
Flexibility in workflows also supports last-minute design changes, preventing delays. By integrating planning and real-time coordination, small-batch production can proceed efficiently, meeting both quality and timeline expectations.
11. Benefits of Small-Scale Production
Cost-Efficiency
Small-batch production reduces financial risks by allowing companies to test designs and refine products without the high upfront costs of mass production.Faster Product Development
It accelerates the development cycle by enabling rapid prototyping, testing, and iteration, ensuring quicker market entry with optimized products.Flexibility for Design Adjustments
Small-scale production offers the flexibility to make design changes and improvements based on feedback, enhancing product quality before scaling to mass production.Risk Reduction
By identifying and addressing potential flaws early in the process, small-batch production minimizes costly errors and ensures smoother transitions to large-scale manufacturing.
12. Conclusion
Small-scale production plays a crucial role throughout product development, from concept validation to pilot production and market testing. It offers flexibility, faster iterations, and cost-effective solutions, reducing risks before mass production. Whether refining designs or producing limited-edition products, small-batch manufacturing ensures quality and precision.
At RALLY, we specialize in small-scale production tailored to your needs, helping you bridge the gap between prototype and mass manufacturing. Contact us today to discuss your project and learn how our advanced CNC machining services can accelerate your product development. Let us help you bring your ideas to life with precision and efficiency!
Work with RALLY for CNC Machining Parts
Request a quote for new project today! No minimum order quantity and free samples available!







